Advances in management of esophageal cancer
While the ESOCAN website and blog focus on the epidemiology and prevention of esophageal cancer, this review gives insight into recent and developing approaches to the management of esophageal squamous cell and adenocarcinoma. Key points that the authors highlight include:
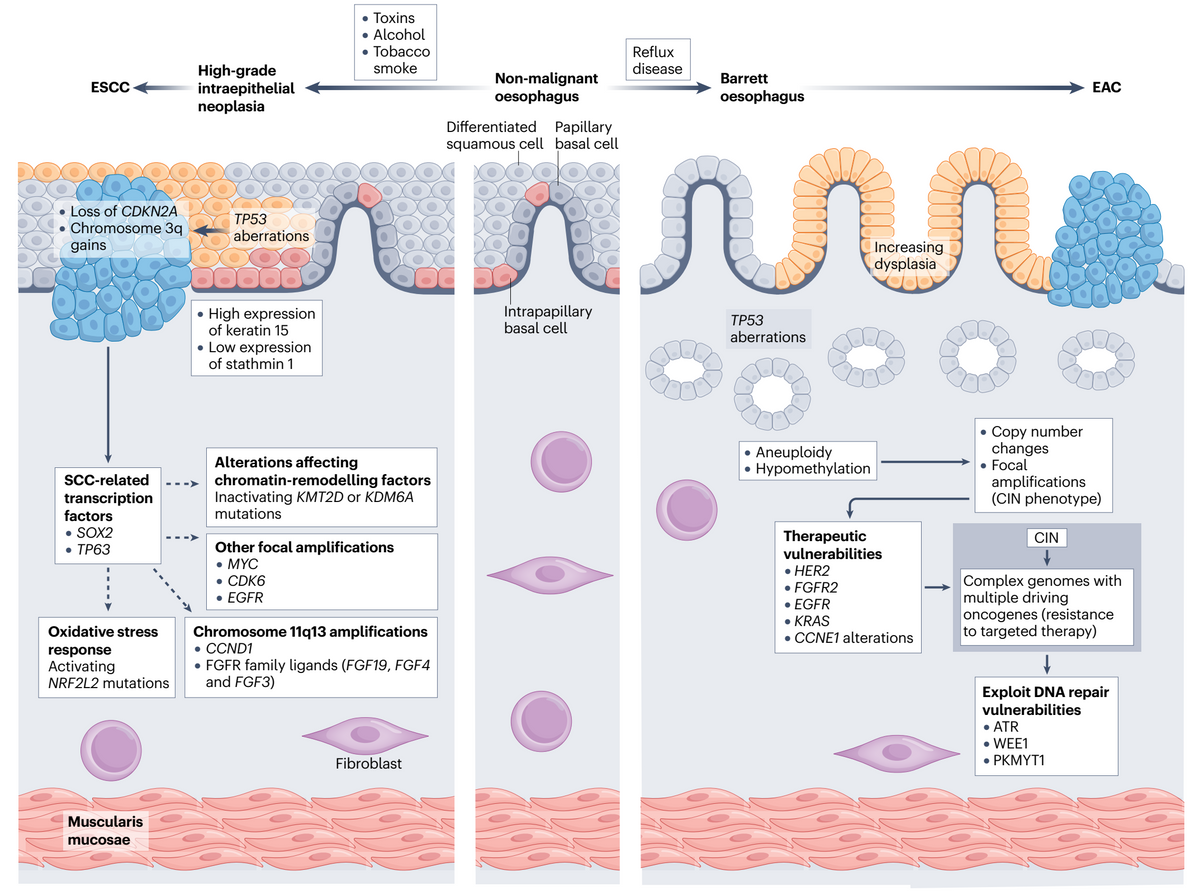
• With advances in molecular profiling technologies, the diferential
mechanistic underpinnings of oesophageal adenocarcinoma and
oesophageal squamous cell cancer have been better defined.
Improved definition and understanding of the molecular alterations
will lead to the discovery of exploitable therapeutic vulnerabilities.
• Novel technologies are being developed for the screening and
surveillance of premalignant lesions, relying on the identification
of the earliest molecular changes in neoplastic transformation.
• The optimal management approach for localized oesophageal
cancer continues to rely on a multidisciplinary team approach, and
advances have been made in each of the subspecialties involved in
the care of patients with this disease.
• Endoscopic resection is a curative option for patients with low-risk
stage T1a–b cancers; for other patients with localized oesophageal
cancers, minimally invasive surgical techniques, improved
perioperative care and improved radiotherapy techniques can reduce
surgical morbidity without compromising oncological outcomes.
• Immune-checkpoint inhibitors and their combinations with
chemotherapy improve survival in patients with advanced-stage
oesophageal cancers.
• The development of novel targeted therapies and immunotherapies
will continue to shape the treatment paradigms of oesophageal
cancers for years to come.
Improving outcomes in patients with oesophageal cancer
Manish A Shah, Nasser Altorki, Pretish Patel, Sebron Harrison, Adam Bass, Julian A Abrams
Abstract
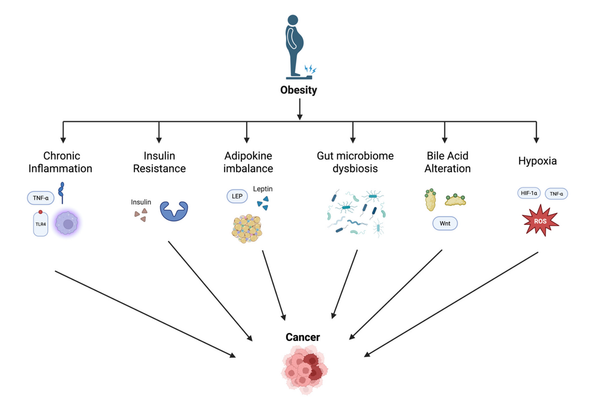
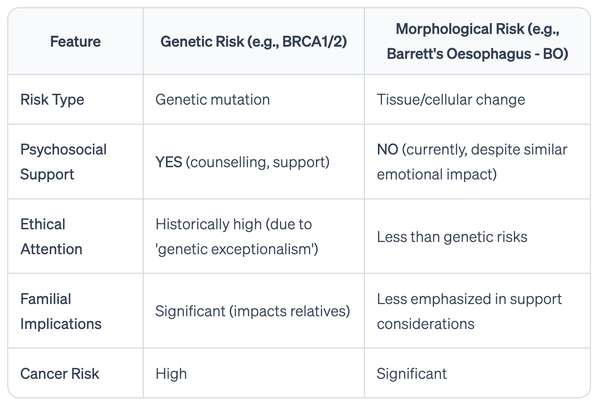
The care of patients with oesophageal cancer or of individuals who have an elevated risk of oesophageal cancer has changed dramatically. The epidemiology of squamous cell and adenocarcinoma of the oesophagus has diverged over the past several decades, with a marked increase in incidence only for oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Only in the past decade, however, have molecular features that distinguish these two forms of the disease been identified. This advance has the potential to improve screening for oesophageal cancers through the development of novel minimally invasive diagnostic technologies predicated on cancer-specific genomic or epigenetic alterations. Surgical techniques have also evolved towards less invasive approaches associated with less morbidity, without compromising oncological outcomes. With improvements in multidisciplinary care, advances in radiotherapy and new tools to detect minimal residual disease, certain patients may no longer even require surgical tumour resection. However, perhaps the most anticipated advance in the treatment of patients with oesophageal cancer is the advent of immune-checkpoint inhibitors, which harness and enhance the host immune response against cancer. In this Review, we discuss all these advances in the management of oesophageal cancer, representing only the beginning of a transformation in our quest to improve patient outcomes.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.