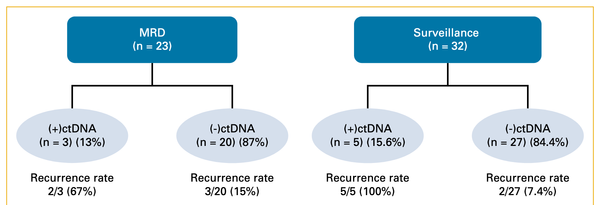
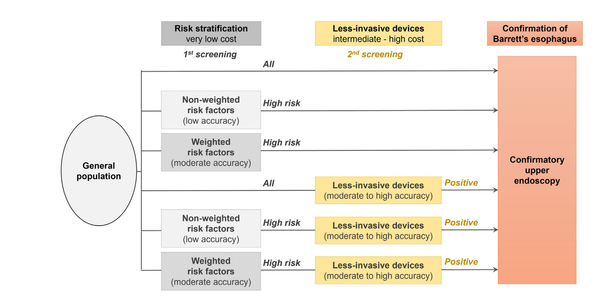
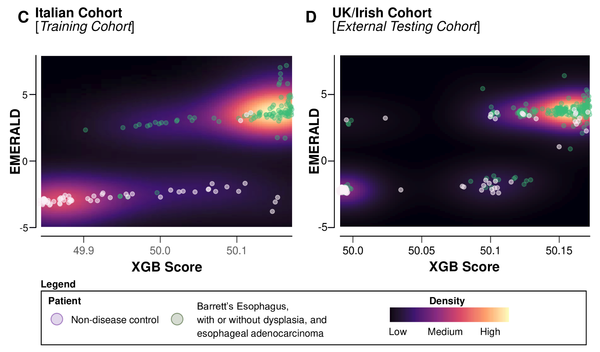
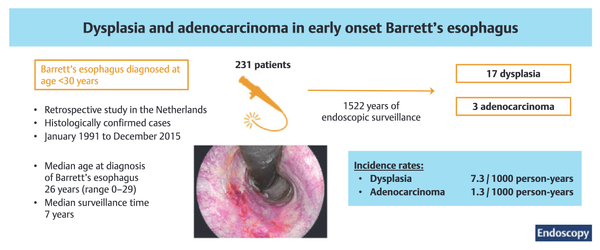
AI in screening and diagnosis of upper GI cancers and precursors
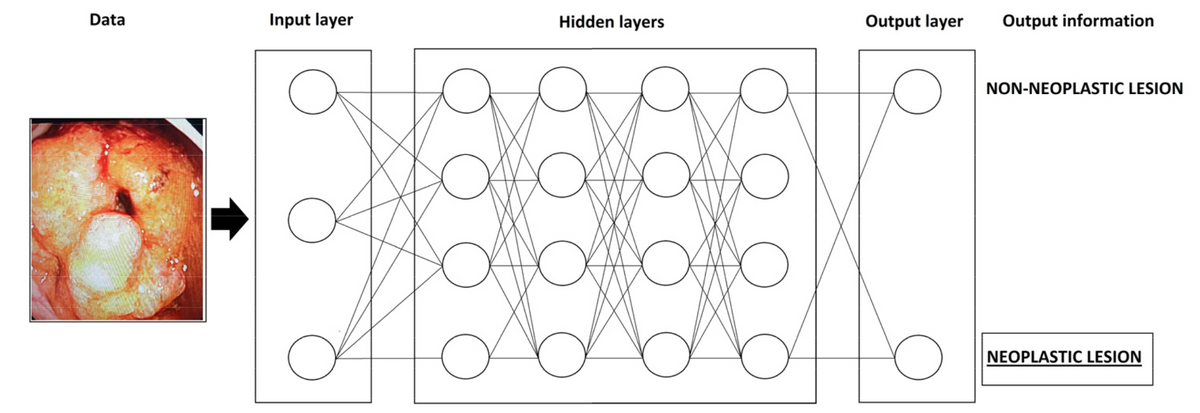
There is currently a great deal of interest in the role of Artifical Intelligence (AI) in medicine, particularly in specialties involving visualization. Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy, employed in the screening, surveillance and diagnosis of esophageal and gastric cancer and their precursors, is one such area that is especially promising in increasing the diagnostic accuracy and quality of this assessment. This report by Dr. Popovic and colleagues from Serbia provides a very readable summary of the approach and recent results of its clinical application in detecting malignant and premalignant lesions.
The Importance of Artificial Intelligence in Upper Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.
Popovic D, Glisic T, Milosavljevic T, Panic N, Marjanovic-Haljilji M, Mijac D, Stojkovic Lalosevic M, Nestorov J, Dragasevic S, Savic P, Filipovic B.
Abstract
Recently, there has been a growing interest in the application of artificial intelligence (AI) in medicine, especially in specialties where visualization methods are applied. AI is defined as a computer’s ability to achieve human cognitive performance, which is accomplished through enabling computer “learning”. This can be conducted in two ways, as machine learning and deep learning. Deep learning is a complex learning system involving the application of artificial neural networks, whose algorithms imitate the human form of learning. Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy allows examination of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum. In addition to the quality of endoscopic equipment and patient preparation, the performance of upper endoscopy depends on the experience and knowledge of the endoscopist. The application of artificial intelligence in endoscopy refers to computer-aided detection and the more complex computer-aided diagnosis. The application of AI in upper endoscopy is aimed at improving the detection of premalignant and malignant lesions, with special attention on the early detection of dysplasia in Barrett’s esophagus, the early detection of esophageal and stomach cancer and the detection of H. pylori infection. Artificial intelligence reduces the workload of endoscopists, is not influenced by human factors and increases the diagnostic accuracy and quality of endoscopic methods.