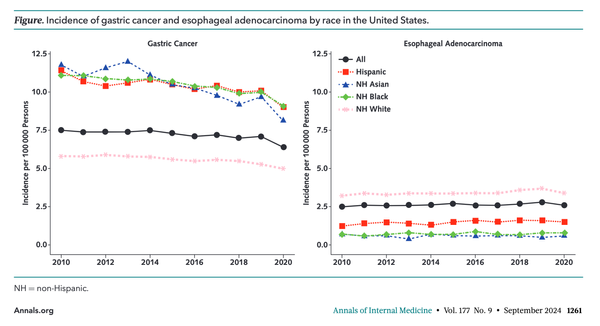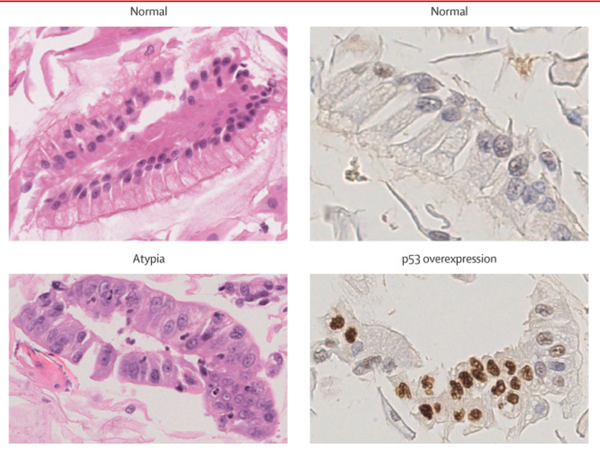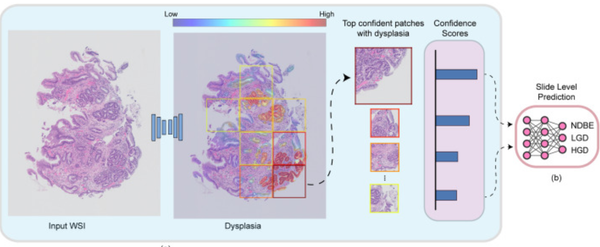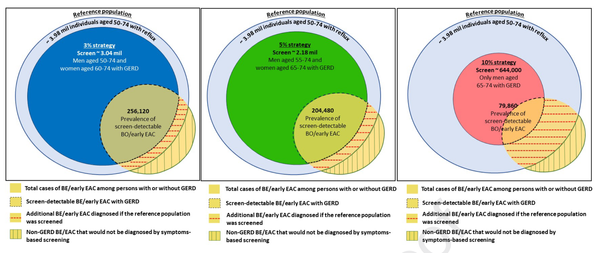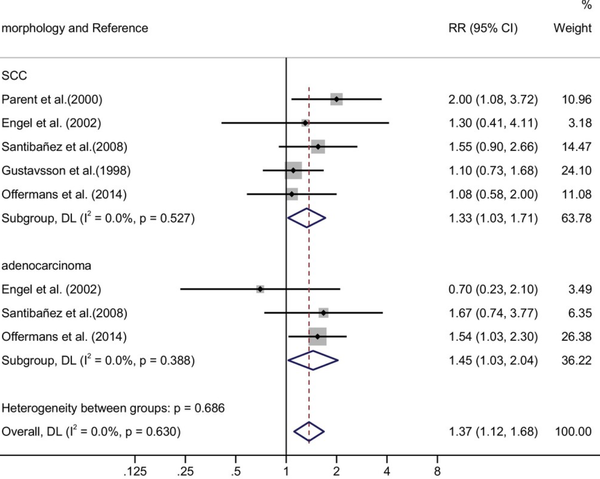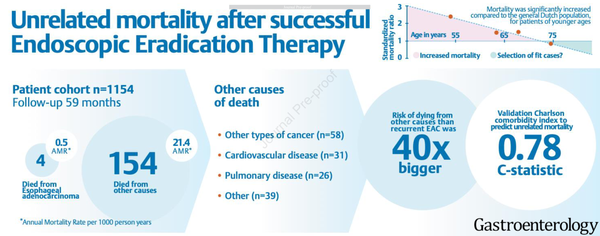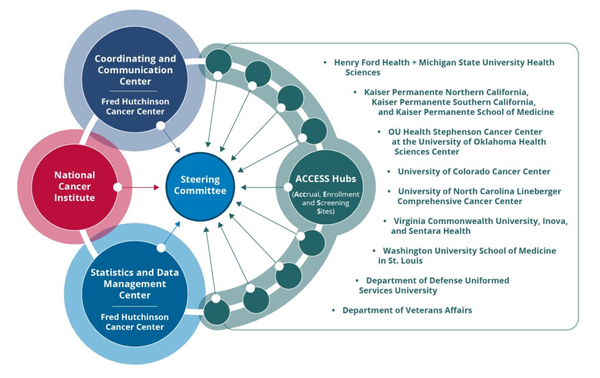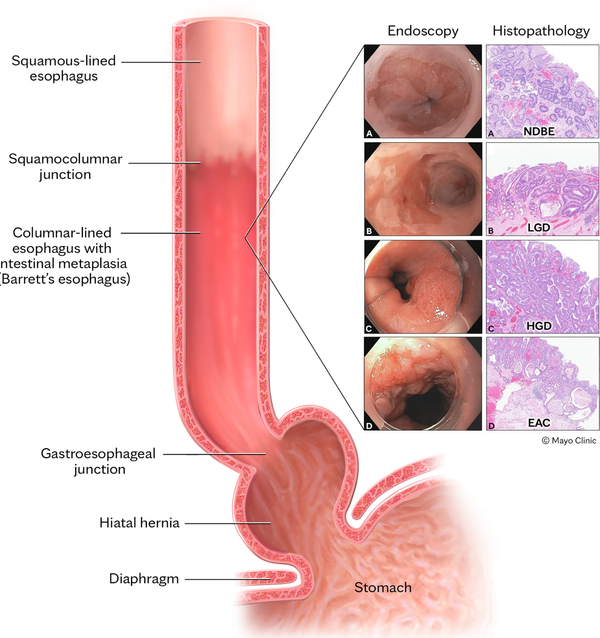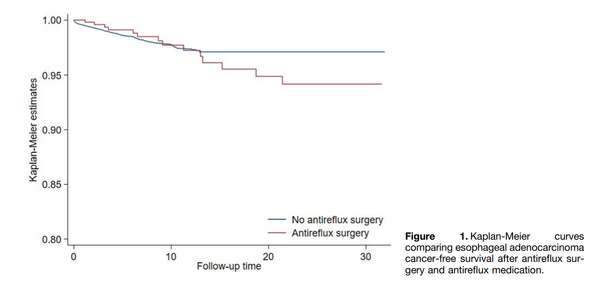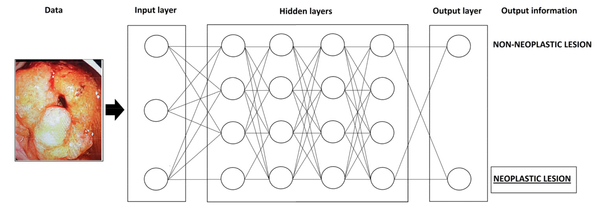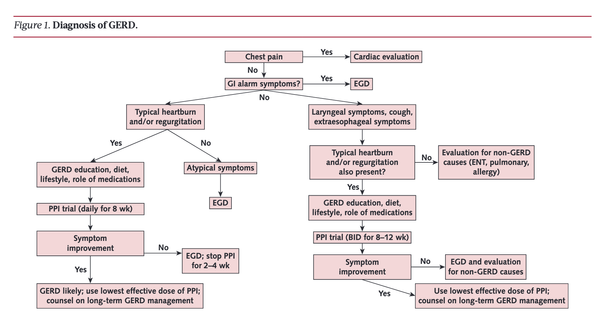
Diagnosis and management of GERD
While most adults occasionally experience symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux, such as heartburn and regurgitation, approximately 20% (30 million people in the U.S.) experience these symptoms more frequently, ranging from once a week to multiple times a day. (1) Complications associated with GERD can include esophageal strictures, ulcers, and even